Key Differences and Implications
In the world of cryptocurrencies, the terms “coin” and “token” are often used interchangeably, but there are some distinct differences between the two. A coin is a digital asset that operates on its own blockchain, which is a decentralized, distributed ledger. Examples of coins include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin. Coins typically have their own unique code and operate independently of other cryptocurrencies. On the other hand, a token is a digital asset that is created and operates on top of an existing blockchain, such as Ethereum. Tokens are often created to represent a specific asset, such as a share in a company or a unit of a commodity. They can also be used to provide access to a particular service or product, or to enable certain functionalities within a blockchain network. While both coins and tokens are used as digital assets, their functionalities and technologies are different.
Understanding cryptocurrency coins
As a medium of exchange, cryptocurrencies offer a fast, secure, and decentralized alternative to traditional payment methods, such as bank transfers and credit cards. They can be used to purchase goods and services online and offline, and some businesses even accept cryptocurrencies as a form of payment. As a store of value, cryptocurrencies are not subject to the inflationary pressures that fiat currencies face, and their value can appreciate over time. Finally, cryptocurrencies are often used as a speculative investment, with traders buying and selling coins in the hopes of profiting from price fluctuations. However, due to the high volatility and risks associated with cryptocurrencies, it is essential to conduct thorough research and understand the market before investing.
Differences Between Coins and Tokens
On the other hand, a cryptocurrency token is a unit of value that is created and managed on an existing blockchain, such as Ethereum. Tokens do not have their own blockchain but are instead built on top of an existing blockchain infrastructure. Tokens are often created as part of an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or Initial Token Offering (ITO) to raise funds for a new project or startup.

Purposes Of Cryptocurrency Tokens
Tokens are often created through initial coin offerings (ICOs), in which developers raise funds for their projects by selling tokens to investors. These tokens can represent a variety of assets, such as real estate, art, or intellectual property rights, and their value can fluctuate based on market demand. In addition, tokens can be programmed with smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. This allows for the automation of complex agreements and eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Overall, the versatility and programmability of tokens make them a valuable tool for blockchain-based applications and the creation of decentralized ecosystems.
In summary
While both coins and tokens are used as units of value in the crypto ecosystem, coins typically have their own blockchain, while tokens are built on top of an existing blockchain. Coins are generally used for general currency purposes, while tokens are often created to serve a specific function within a larger ecosystem.
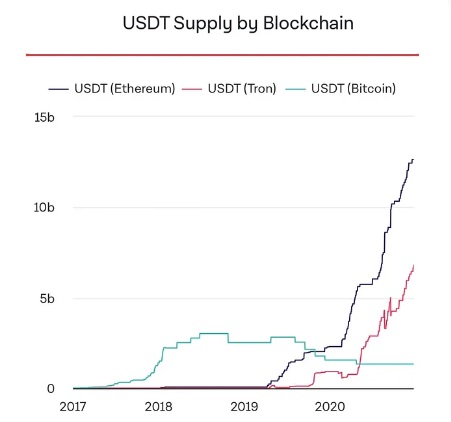
USDT on Different Blockchain Networks
USDT (Tether) is a popular cryptocurrency that is pegged to the US dollar. It is used by traders and investors around the world for its stability and liquidity. However, it is important to note that USDT is available on different blockchain networks, and these networks can differ in various ways.
USDT: Blockchain Options and Differences
One of the main differences between USDT on different blockchain networks is the blockchain technology that is used. USDT is available on several blockchain networks, including Ethereum, Tron, Binance Smart Chain, and others. Each of these blockchain networks has its own unique characteristics, such as transaction speeds, security features, and token standards.
USDT Availability Varies Across Blockchains
Another important difference is the availability of USDT on different blockchain networks. While USDT is available on many different blockchains, the supply of USDT may not be the same on each network. For example, the supply of USDT on the Ethereum network is significantly larger than the supply of USDT on the Tron network.
Blockchain Speed and Fees Comparison
The transaction fees and network speeds can also differ between blockchain networks. For instance, the Ethereum network is known for its high transaction fees due to the high demand for its network, leading to network congestion. This has led to many developers and users looking for alternative blockchain networks with faster transaction speeds and lower fees. One of the blockchain networks that have gained popularity in recent years is the Binance Smart Chain, which offers faster transaction speeds and lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum.
USDT Incompatibility Across Blockchains
It is also important to note that USDT on different blockchain networks may not be compatible with each other. This means that USDT on the Ethereum network cannot be used on the Tron network, and vice versa. Traders and investors must ensure that they are using the correct USDT token for the blockchain network they are using.
In conclusion
While USDT is available on different blockchain networks, it is important to understand that these networks can differ in various ways. Traders and investors must do their due diligence and understand the differences between USDT on different blockchain networks before they decide to trade or invest in USDT. By doing so, they can make informed decisions and ensure that they are using the correct USDT token for their needs.